University of Southeastern Philippines
Obrero, Davao City
INTRODUCTION
Isolation chairs , it is easy to think that learners in the classroom can be able to spend an hour a day sitting in a school chair as if it’s an easy task to accomplish, however, it’s the other way around for learners with an autism spectrum disorder.
In typical circumstances they couldn’t hold that long because there are distractions that trigger their focus and in-seat behavior such as interruptions in the classroom, resistance and and too much movement.
These kinds of actions can cause learners’ academic performance issues. As I observed in the class of ASD it emphasizes how crucial it is to use appropriate modified isolation chairs and tables in the classroom.
To persist focus, learners with ASD require modified isolation chairs in the classroom which they cant resist but persist more focus on the activity.
In the United States according to a survey, inappropriate classroom behavior is a serious problem for teachers, with 80% of respondents saying it affects students at their schools (Gomez, 2005).
They discovered that the participant’s behavior had improved, and they cited the capacity to maneuver on the ball as a crucial element (Fedewa & Erwin,2011).
In Davao City, some teachers in the autism department at Davao City Special School use alternative seats called “isolation chairs.” Although little research supports this intervention, their experiences show that isolation chairs help them manage learners’ in-seat behavior and increase focus.
Therefore, this study aims to provide an action to the problem of learners resistance and persist more focus in class. A viable solution to this issue which to incorporate an isolation chairs for the teacher to utilize as a support alternative device to lessen the opportunity for movement.
This action research will be beneficial to the Sped teacher’s , parents and future researchers as they can get research based information when it comes to effectivity of isolation chairs and most of all this action research will help the learners to get an intervention for their in-seat behavior.
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
The related literature has different forms wherein it comes from different resources such as, books, journals, articles, news, and other pertinent resources which are highly relevant and related to the premises of research. It honors the different formulated and come-up studies of previous creators and researchers.
In this part of the study, there was presumption that when the researchers mentioned the name of the author stating the previous work in the field study presumably, the author has evaluated, read and assimilated such work. The related literature of this study would enable the readers to fully understand the contents of the study posits by the researcher. The content specified herein will tackle the literature from the great – famous authors that supplied the information’s and ideas about the present study.
Class learners with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism spectrum disorder refers to differences in the brain development and process information which has an effect to the social, communication and behavior challenges (Gavin, Mary L., 2018).
As a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects a person’s ability to interact and communicate socially with others (Centers for Disease Control and Preventions,2015).
Students with autism exhibited a repetitive and challenging behaviors but, it did not affect the individual’s cognitive ability as autism affects an individual differently and presents with varying degrees of severity.
Records show that students or children with autism may have trouble speaking or may not speak at all.
They often miss class time for doctor visits and therapies. Some seem insensitive or unemotional.
Most students with autism struggle with social skills because crowded classrooms make it hard for them to engage in learning, which creates challenges for their teachers (Fleury et al., 2014).
Truly, students with autism had social discomfort and it can have an attribute to their impairment of their executive functioning system. Autistic students experienced discomfort and anxiety in a changing situation (Perfitt, 2013).
But they continue to focus on the individual puzzle pieces rather than seeing the whole picture formed by putting them together.
Autistic children struggle to make progress in literacy skills, such as sight word recognition (Muchetti, 2013). They may also have difficulty decoding text because they struggle with reading comprehension (Whalon & Hart, 2011).
In Manolis, Liz (2016) that their tips for teaching students with autism such as, teachers should use visual, avoid sensory overload, teachers should directly teach social skills, teachers should be predictable and they should use language concrete and teachers should treat students as individuals.
Traditional Seating
Since the eighteenth century, the classroom setting was already the standard element of the physical environment that has effect of traditional arrangements and seating on classroom behavior (Bicard, Ervin, Bicard, & BaylotCasey, 2012). In traditional seating refers to an arrangement of equidistant rows with identical desks and hairs.
Forms of Alternative Seating
Standing desks
The standing desks is one the most accessible forms of alternative seating wherein it allowed the students to stand with the option of sitting on a chair. According to Benden et. al (2011) that the students able to sit and
stand at their discretion is a stand-biased which is not expensive alternatives to traditional seating. Also, it has the ability to interrupt sedentary behavior pattern. In the study of Brenden et al. (2011)
That those students who employ the standing desks had a significant increase in energy expenditure that those who did not utilize the stand-biased desks.
Where it discovered the effect of standing desks on children’s sit and stand behaviors, academic performance, physical activity levels, and classroom behaviors.
It revealed that the time spent sitting decreased physical activity and the time standing increased positive academic behavior increased in most studies.
Foot fidgets
In Hartanto, Kraft, Losif, & Schweitzer (2015) that students should have the opportunity to fidget with predetermined manipulatives such as, silly putty, squishy balls, or Velcro, this fulfills the students’ sensory needs.
The foot fidgets the focus on fidgeting in the classroom appeared as an alternative mode of seating and had an attention to task in the classroom.
It aims to provide sensory input by allowing students to press against the fidget with their foot and it affords students the opportunity to concentrate at elevated levels.
As claimed by Sarver et al., (2015) that students become more restless during reading and mathematics. According to Sarver, Rapport, & Kofler (2015) that the students need to fidget while doing classroom complex cognitive task.
Therapy balls
In fact, it has a sitting discomfort to the academic performance in an elementary classroom.
It revealed in the study of Al-Eisa, Baragadda, & Melam (2013) that those students who used therapy balls
had a significant decrease in discomfort while seated and their problem-based learning scale score increased in all subject areas.
According to Fedewa & Erwin (2011) that through the usage of therapy balls, the fourth and fifth-grade students HAD increased on-task and in-seat behavior.
Thus, the therapy balls really increase in attention within the learning environment as an alternative seating in the classroom (Schiling & Schwartz, 2004). In Sadr (2017) wherein it also discover whether therapy balls,classroom isolation chairs and air cushions affect the classroom behavior of individuals with autism.
Disc ‘o’ sit cushions
The Disc ‘o’ sit cushions is one form of alternative seating which is flat on one side and have a bumpy texture on the other side.
When placed in traditional and isolation chairs, the cushions offer learners an opportunity for increased sensory input and a natural range of movement. In Pfeiffer, Henry, Miller, and Witherell
(2008) wherein it investigated the effectiveness of a type
of dynamic seating system, the Disc ‘O’ Sit cushion for developing attention to task among second-grade students with attention difficulties.
It revealed that the usage of Disc ‘O’ Sit cushion served as an occupational therapy intervention to develop attention in the school setting.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
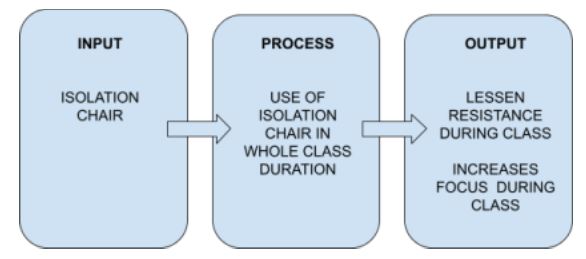
RESEARCH QUESTION
The researchers seek to unravel The Utilization of Isolation Chairs to lessen students’ resistance and persist focus in a class of learners with ASD.
More specifically, this study aims to answer the following questions:
1. What is the demographic profile of the respondents in terms of: 1.1. Age
1.2. Sex?
2. What are the challenges of in-seat to the behaviors of students with autism?
3. What is the influence of integrating isolation chairs that would pacify the behaviors of students with autism?
- What possible interventions can teachers provide to students with autism spectrum disorder in the classroom?
SCOPE AND LIMITATION
This study is focused on the positive effects of the utilization of an isolation chairs
that can lessen students’ resistance and persist focus in class.
This study is intended for the learners of Davao City Special School
under the department of Autism Spectrum Disorder, grade level Kinder and Primary section Blue.
Furthermore, the area to be investigated in this study
will only focus on the in-seat behavior of the learners without the use of isolation chairs
and the modified in-seat behavior after utilizing the isolation chairs.
Afterward, the researchers will carefully observe and analyze
both data to identify the positive effects of lessening learners’ resistance and persistent focus in class activities
RESEARCH DESIGN
This study will use the Action Research approach in order to answer and try to solve the existing problem which is to increase focus in class activities while
lessing their movement by utilizing isolation chairs.
According to Bradbury and Reason 2001, as cited by Miller, et al., 2003, this research design is well suited to this study because action research is designed
to create a practical solution to issues and problems concerning the people, they also added that action research is process concerned with developing practical knowledge and solution to
an issue which believed to be emerging at this moment. Moreover, action research is the best method for this kind of study because action research is an emergent process of creating knowledge
to be applied and address real organizational issues or problems, action research takes place in current situation with a goal
to contribute solution for the development of a specific situation or issue (Coghlan, 2019).
SAMPLING
The participants of this study are the students from Davao City Special School under the department of Autism Spectrum Disorder,
Grade level Kinder and Primary Section Blue.The students were selected to use the isolation chairs who have the in-seat behavioral problem.
Purposive sampling was utilized in this study to allow the researchers to freely select respondents who could successfully provide accurate data
for the study’s objective which is to lessen resistance and persist focus in class. According to Robinson (2014)
Purposive Sampling method is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment
when choosing the respondents for the study which the researchers think can give useful information for the study.
SOURCES OF DATA
The instrument that will be utilize by the researcher
to collect data from the participants will be through a form of observation of learners modified behavior when utilizing the isolation chair during their class.
The observation will last for a week so that researchers
can observe and collect the consistent behavior of participants when using the isolation chairs.
Researchers will observe the after and before in-seat behavior of learners as they use the isolation chairs.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATION
Clear initiatives will be taken and a number of measures will be enacted to strengthen research ethics as a pillar of systematic investigation.
The voluntary participation is made by the participants and is not compelled by researchers, informed consent will be humbly sent to the concerned individuals.
As requirements for honesty, Confidentiality and Anonymity participants name and identity will be pseudonymized pursuant to the Republic Act No. 10173, otherwise known as the Data Privacy Act.
Protection of the integrity of research participants and informants is a particularly important ethical norm in research,
including in special-needs education studies. This focuses on protection against various forms of risk involved in participation
in research including concerns for preventing stigmatisation of particular populations or groups according to Matthias Kaiser (2019).
Finally, authors of the studies and literature used in this study will be rightly recognized and cited.
DATA ANALYSIS
Thematic analysis approach will be employed in this study to analyze the collected data that involves exploring data for interpreting and reporting on repeating patterns or themes (Braun and Clarke 2006). It is a method for identifying, analyzing, organizing, describing, and reporting themes found.
Furthermore, King (2004) claimed that thematic analysis is a useful method for examining the perspectives of different research participants, highlighting similarities and differences, and generating unanticipated insights. Analysis begins with the collection, familiarization and management of the data. Themes are generated inductively from the patterns in the data that are informed by sourcing existing knowledge from the literature. To contextualize and represent the findings, the data is represented as cohesive snapshots that provide detailed pictures of the analyzed data. The research questions are ultimately addressed through the interpretations, as woven patterns found in the data. This thematic approach confirms the active role of the qualitative researcher when identifying patterns across the dataset and requires the researcher to be deliberative, reflective, and thorough (Braun & Clarke, 2006).
REFERENCES
Al-Eisa, E., Buragadda, S., & Melam, G.R. (2013). Effect of therapy ball seating on learning and sitting discomforts among Saudi female students. BioMed Research International,
Benden, M.E., Blake, J.J., Wendel, M.L., & Huber, J. C. (2011). The impact of stand-biased desks in classrooms on calorie expenditure in children. American Journal of Public Health, 101 (1433 -1436.
Decisions. American Educational Research Journal.
https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831210380788
Braun V, Clarke V. 2006. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 3(2):77–101
Centers for Disease Control and Preventions. (2015). Facts about ASD. Retrieved March 25,2015, from
http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/facts.html
Coghlan, D. (2019). “Doing Action Research in Your Own Organization”. Retrieved on January 1, 2022 from https://bit.ly/3FLUgTg
Fedewa, A. L., & Erwin, H. E. (2011). Stability balls and students with attention and hyperactivity concerns: Implications for on-task and in-seat behavior. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 65, 393-399
Hartanto, T. A., Kraft, C. E., Losif, A.M., & Schweitzer, J. B. (2015). A trial-by-trial analysis reveals more intense physical activity is associated with better cognitive control performance in
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Neuropsychology, 22(5), 618-626. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2015.1044511.
Development, and Education, 60, 347-362.
Philippines guarantees learners with disabilities with free basic education. (2022, March 16). www.philstar.com.
Muchetti, C. A. (2013) Adapted shared reading at school for minimally verbal students with autism.
Pfeiffer, Henry, Miller, and Witherell (2008). Effectiveness of Disc ‘O’ Sit
cushions on attention to task in second-grade students with attention difficulties. Am J Occup Ther. 2008 May-Jun;62(3):274-81. doi: 10.5014/ajot.62.3.274.
Robinson R.S. (2014) Purposive Sampling. In: Michalos A.C. (eds) Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0753-5_2337
SADR, N. M., Haghgoo, H. A., Samadi, S. A., Rassafiani, M., Bakhshi, E., & Hassanabadi, H. (2017). The Impact of Dynamic Seating on Classroom Behavior of Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Iranian journal of child neurology, 11(1), 29.
Sarver, D. E., Rapport, M.D., & Kofler, M. J. (2015). Hyperactivity in attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Impairing deficit or compensatory behavior?Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 43(7), 1219-1232. doi:10.1007/s10802-015-0011-1
Schilling, D. L. & Schwartz, I. S. (2004). Alternative seating for young children with autism spectrum disorder: Effects on classroom behaviors. Journal of Autism Developmental Disorders, 34(4), 423.
doi:10.1023/B:JADD.0000037418.48587.f4
Summer, R. (1969). Personal Space. Englewood Cliffs, NJ. Prentice Hall, 1969
Tunstall HR. Effects of Alternative Seating on the Academic Engagement of Children With Autism. East Carolina University; 2010. [Google Scholar]

I’m Ethan Richards, the guy running the show at “Acknowledgment Templates.” I’ve been playing with expressions and formats to make acknowledgment writing a whole lot of fun. Over at Acknowledgment Templates, we’re here to make your acknowledgment section incredible. Let’s add some professionalism and gratitude to your project together!












